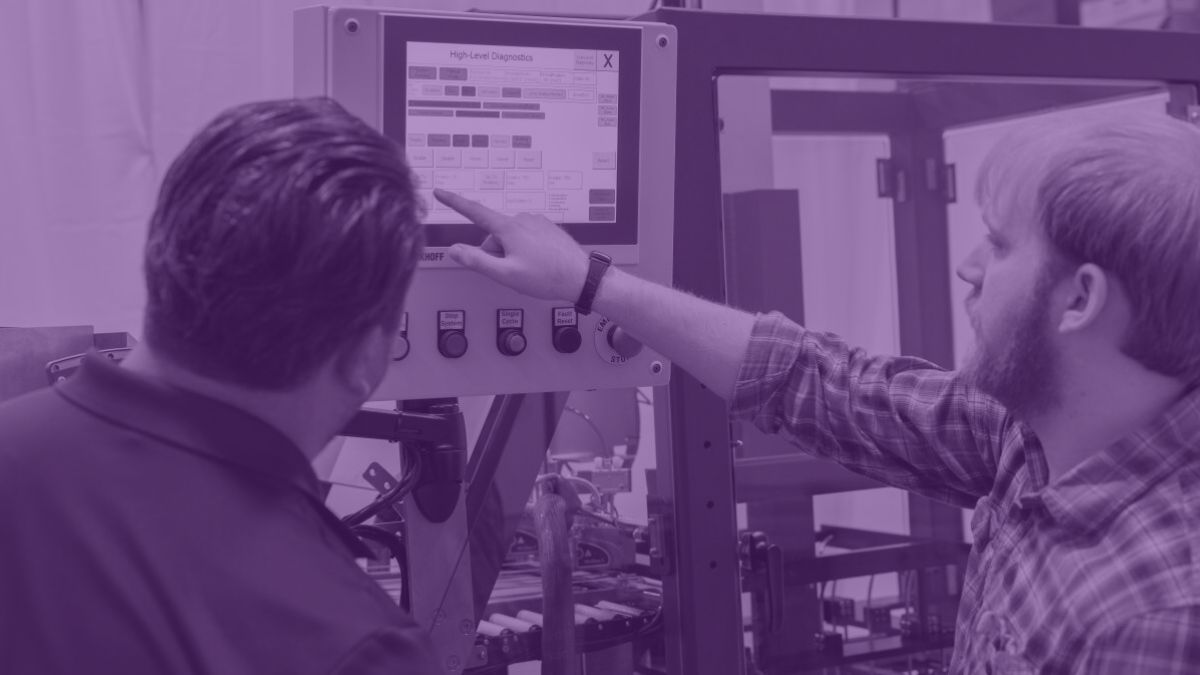
Installation day is exciting. The equipment arrives, the technicians get everything running, and suddenly your packaging line is doing things that used to require three operators and constant oversight.
But here’s what separates a successful automation investment from an expensive mistake:
- What happens six months later when production demands change?
- What about a year later when you need to add a new SKU?
- Or three years down the road when regulatory requirements shift?
Automation success doesn’t end at installation.
The companies getting the most value from their integrated automation systems aren’t just buying machines—they’re building relationships with partners who understand that production challenges evolve, systems need optimization, and the difference between uptime and downtime often comes down to who picks up the phone when you call.
Automation Success Starts Long Before Installation
Automation projects often start with a problem, which a good partner will help you approach from every angle. They’ll identify upstream processes that will affect a new install and recognize bottlenecks that need to be considered through a new lens. A true collaborator will help you develop a project from square one, and support you in making smart and proactive decisions throughout the process.
The best automation partners will guide you through the entire lifecycle, not just the technical bits:
- Analysis, discovery, and optimization
- Choosing and future-proofing the right technology
- Engineering, architecture, and building
- Testing and quality assurance
- Installation, training, and change management
- Long-term support and evolution
Automation is a huge investment and who you work with can make or break both the experience and your ROI. The right partner will guide solution development so that every small but critical detail is considered.
Automation Success Extends Far Beyond Installation
Every production line goes through phases. The initial installation gets equipment running and operators trained, but the real performance story unfolds over time.
- Product mix changes
- Throughput requirements increase
- New compliance standards emerge
- Materials from suppliers shift slightly, affecting how products feed or how labels adhere
A transactional equipment vendor delivers a machine, provides basic training, and moves on to the next sale. When issues arise or optimization opportunities appear, you’re on your own. This approach might work for simple standalone equipment, but it falls apart when you’re running custom automation systems designed to fully integrate with your production line.
A true automation partner stays engaged. They track how systems perform in real-world conditions, help troubleshoot challenges before they become costly problems, and work with your team to fine-tune processes as production needs evolve. This ongoing relationship protects your investment and ensures your automation continues delivering value year after year.
Integration Challenges Across Existing Production Lines
Integrating new automation into an existing production environment is more complex than installing a standalone machine. Your new friction feeder needs to communicate with upstream conveyors. Your labeling automation must sync with downstream inspection systems.
Timing, product flow, and data exchange all need to work seamlessly across equipment from different manufacturers, often spanning different technology generations. These integration challenges rarely show up in factory acceptance tests.
They emerge when systems run at full production speed with real products, real operators, and real-world variables. A long-term partner understands this. They don’t just configure equipment to work in isolation—they engineer solutions that fit into your complete production workflow.
MFT Automation approaches every project with this systems-thinking mindset. Whether you’re adding a hygienic friction feeder to an existing food packaging line or integrating print and apply labeling systems into a pharmaceutical serialization workflow, we work alongside your team to ensure every component communicates effectively and performs reliably within your broader production ecosystem.
Automation Support, Parts, Upgrades, and Optimization
Production doesn’t stop because a part fails or a software update is needed. This is where ongoing support becomes critical. A true automation partner maintains stock of replacement parts, understands your specific equipment configuration, and can diagnose issues remotely when time matters most.
But proactive optimization goes above and beyond just fixing what breaks, identifying opportunities to:
- improve cycle times
- reduce changeover duration
- enhance product handling based on real-time production analysis
A strong automation partner employs engineers who know your equipment inside and out and can recommend upgrades that extend system life or add new capabilities without requiring complete line replacement.
MFT’s approach includes comprehensive support across the equipment lifecycle. Our engineering team stays familiar with customer installations, our parts inventory ensures critical components ship quickly, and our service technicians understand both the mechanical and integration aspects of your packaging automation solutions. When you call, you’re talking to people who know your system and your production challenges.
Modular System Upgrades vs. Full Line Replacements
Market demands change, and your automation needs to keep pace. The question is whether adapting to change requires replacing entire systems or simply upgrading specific modules. This is where modular system design delivers long-term value.
Well-engineered automation system integration allows targeted improvements without disrupting your entire production line.
- Need faster throughput? Upgrade the feeder servo controls.
- Adding a new product size? Swap in a different label applicator head.
- Implementing serialization? Integrate track and trace components into your existing line architecture.
Modular upgrades minimize downtime, reduce capital expense, and let you evolve production capabilities as business needs change. At MFT Automation, we design industrial automation solutions with this modularity in mind from the start. Our friction feeders, labelers, and integrated systems use standardized interfaces and flexible configurations that support both current production requirements and future expansion.
How MFT Works Alongside Customers as Production Evolves
Long-term partnerships are built on communication, responsiveness, and shared goals. When production challenges arise or opportunities for improvement appear, the right partner is already familiar with your operation and invested in your success.
MFT Automation maintains relationships with customers long after installation. We track equipment performance, provide training as your team grows, and stay available when you need technical guidance or troubleshooting support. Our engineering team works with customers to optimize existing systems, retrofit new capabilities, and adapt automation to changing production requirements.
This ongoing collaboration has helped customers across pharmaceutical, food, printing, and cannabis packaging operations improve line efficiency, meet new regulatory standards, and scale production without major reinvestment.
The difference comes down to partnership—working together to solve real production challenges rather than simply selling equipment and moving on.
Automation as a Strategic Investment, Not a One-Off Purchase
The value of automation compounds over time when systems are properly maintained, optimized, and upgraded. What starts as a solution to a specific bottleneck becomes a flexible production platform that adapts to new products, new regulations, and new market demands.
Viewing automation as a strategic investment changes how you evaluate vendors. Initial equipment cost matters, but total cost of ownership (including support, parts availability, upgrade paths, and long-term reliability) will determine real value. A partner who stays engaged protects that investment and helps you extract maximum value from every automation dollar spent.
At MFT Automation, we’ve spent decades engineering packaging automation solutions that deliver reliable performance across demanding production environments. But equipment is only part of the equation. The real difference comes from how we work with customers throughout the equipment lifecycle—from initial system design through installation, optimization, and ongoing support.
Your production challenges don’t stay the same. Your automation partner should support your evolving needs as business changes. Whether you’re exploring your first automation system or optimizing an existing integrated line, the right partnership makes all the difference.
Ready to Connect with a Premier Automation Partner?
If you’re evaluating custom automation systems for pharmaceutical, food, printing, or cannabis packaging operations, let’s talk. Our team is ready to discuss your production challenges and explore how integrated automation can provide value today and adapt to your future needs.
Contact MFT Automation to start a conversation with our engineering team.